Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) for Infertility Treatment
Reviewed by: HU Medical Review Board | Last reviewed: March 2025 | Last updated: March 2025
Endometriosis can make it hard to get pregnant. Endometriosis causes tissue like the lining of the uterus to grow outside the uterus. This growth can cause pain and damage to your reproductive organs. If you have endometriosis and want to have a baby, assisted reproductive technology (ART) might be an option.1
What is assisted reproductive technology (ART)?
ART is a group of medical procedures. These procedures help people who cannot get pregnant on their own. ART uses special techniques to handle eggs and sperm. The goal is to help a fertilized egg grow into a baby.2
Types of assisted reproductive technology (ART)
There are several types of ART. Here are some of the most common:2
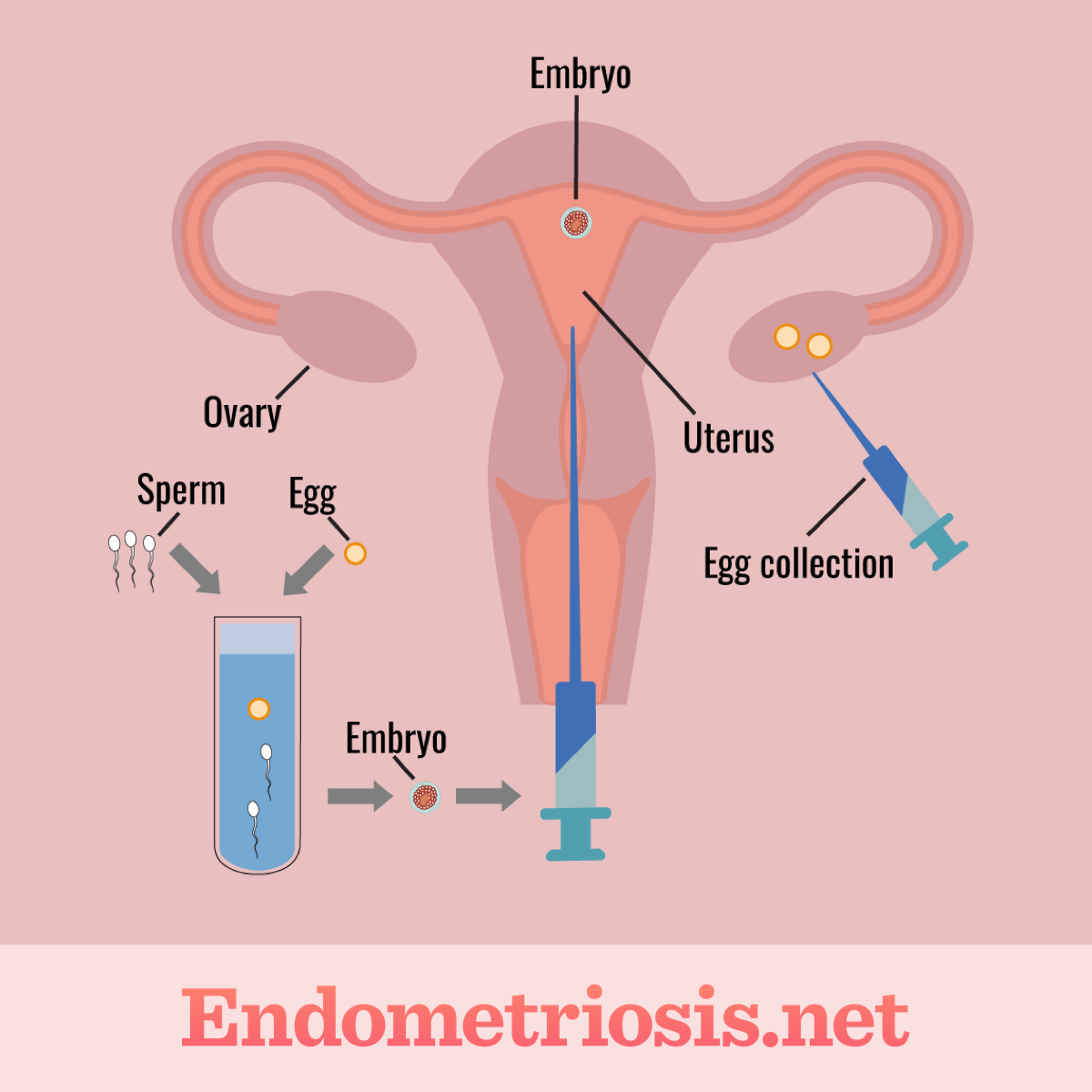
In vitro fertilization (IVF)
Figure 1. In vitro fertilization procedure
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is the most common type of ART. During IVF, multiple eggs are fertilized by sperm outside of the body in a lab. These eggs and sperm cells can come from the couple trying to give birth or from donors. Multiple fertilized eggs (embryos) are then implanted back into the uterus of the person they came from or into a gestational carrier or a surrogate.2-4
From there, these embryos may lead to pregnancy. In some cases, IVF may be used as a means of preserving fertility. Eggs and sperm can be harvested from the body and frozen in order to store them for later use. This method may be used for those who might be undergoing treatment that may impact their fertility, eggs, or sperm, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy for cancer.2-4
The main steps in IVF involve:2-4
- Taking drugs to induce ovulation
- Retrieving the eggs through a minimally invasive procedure
- Collecting a sperm sample
- Joining the egg and sperm in a lab to promote fertilization
- Transferring the embryos into the uterus
Third party-assisted ART
In some cases, a donor or gestational carrier may be needed for pregnancy. There are many reasons why donor sperm or eggs and/or a surrogate or gestational carrier may be used.2
If a person has a condition that causes them to be unable to carry a baby, a surrogate or gestational carrier may be needed. If they have a condition that affects the quality of their eggs, they may need donor eggs. This may also be the case for male partners who have issues with the quality or quantity of their sperm. The process of IVF can be completed with biological or donor eggs and/or sperm and implanted back into the person trying to give birth. Or, they can be transferred into a carrier.2
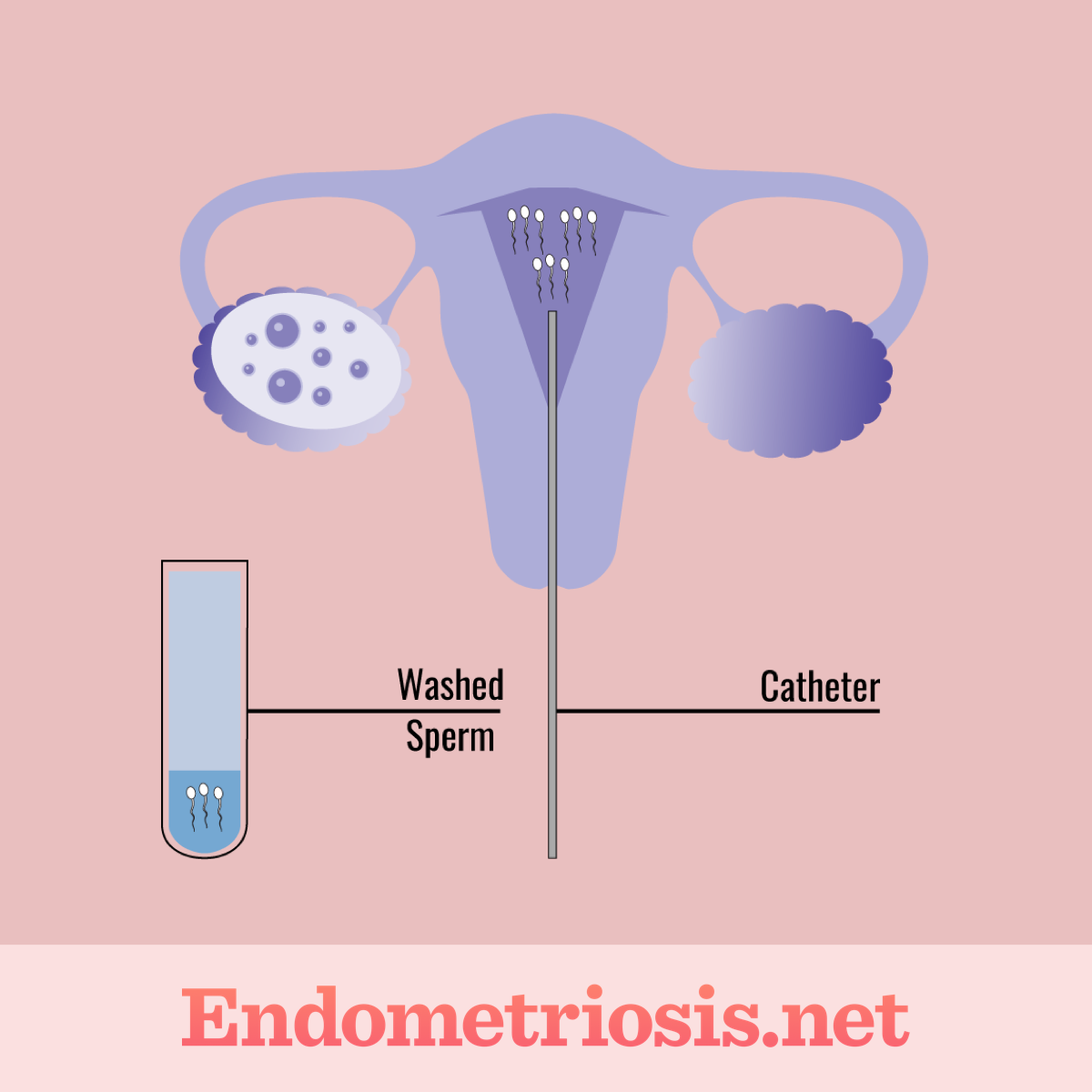
Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
Figure 2. Intrauterine insemination procedure
As mentioned, not all outlets agree as to whether IUI is considered a true ART since the inseminated eggs are not being handled in any way. However, IUI is designed to help induce pregnancy for people or couples struggling to become pregnant or who need donor sperm.2,5,6
IUI, also called artificial insemination, involves delivering sperm directly into the uterus while a person is ovulating. When a person is ovulating, they release an egg, or eggs, from the ovaries. This egg then travels through the fallopian tubes and into the uterus. If the egg is fertilized by a sperm, pregnancy could result. By delivering sperm directly into the uterus around the time of ovulation via IUI, it is possible to increase a person's chances of becoming pregnant.2,5,6
Even if a person is using IUI, the eggs still need to make it through the fallopian tubes and into the uterus to meet the inserted sperm and potentially implant into the uterine wall for pregnancy to occur. If a person has a condition that prevents this process from happening, IUI may not be an option. Other methods, such as IVF, may need to be considered. The critical piece of IUI is timing. It is important to inseminate a person while they are ovulating for the highest chance of becoming pregnant.5,6
What to expect from ART
ART is a process. It often takes several steps. Here is what you might expect:1,2
- Testing – Doctors will do tests to check your fertility. They will also check your partner's fertility. These tests help doctors decide which type of ART is best for you.
- Medicine – You may need to take medicine to help your ovaries produce eggs. It can also help prepare your uterus for an embryo.
- Egg retrieval – If you are doing IVF, eggs will be removed from your ovaries. This is a minor surgical procedure.
- Fertilization – In the lab, eggs are mixed with sperm. Or, a single sperm is injected into an egg.
- Embryo transfer – One or more embryos are placed into your uterus. This is a simple procedure.
- Pregnancy test – After the embryo transfer, you will wait a few weeks. Then, you will take a pregnancy test.
ART can be emotionally and physically challenging. Make sure you have support during this time. Talking to a therapist or joining a support group can be very helpful.
Questions to ask your doctor about ART
If you have endometriosis and are interested in becoming pregnant, talk with your doctor. They will likely refer you to a fertility specialist who can answer your questions.1
Here are some questions you can consider during those conversations with your healthcare team:1
- What type of ART is best for me?
- What are the chances of getting pregnant with ART?
- What are the risks of ART?
- How much does ART cost?
- How many cycles of ART might I need?
- What medications will I need to take?
- What are the side effects of the medications?
- What support services are available?
- How does endometriosis affect my chances of success with ART?
- Are there any lifestyle changes I should make?
The more information you have, the better you can understand the process and know which options are right for you.
Hope and support
Endometriosis can make it harder to get pregnant. But, ART can help. Many people with endometriosis have success with ART.
Remember that you are not alone. There are many resources available to support you. Talking to your doctor and finding support groups can help you through this journey.